You are viewing the RapidMiner Hub documentation for version 10.0 - Check here for latest version
RapidMiner Server Overview
RapidMiner Server is a performance-optimized application server where you can schedule and run your analytic processes and quickly return your results. It seamlessly integrates with not only RapidMiner Studio, but other enterprise data sources as well, allowing processes to continually update so that they reflect any changes to external data sources. With shared repositories and version management, contributors throughout your organization can — locally or remotely — collaborate, build interactive apps, and visualize results using HTML5 charts and maps.
Understanding the general infrastructure
There are several main components to a RapidMiner Server configuration:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| RapidMiner Studio | RapidMiner Studio is where you build and edit analytic processes. RapidMiner Studio and RapidMiner Server connect and interact with each other, employing standard protocols. For each instance of RapidMiner Server, you can connect one or multiple RapidMiner Studio clients. |
| RapidMiner Server | Although it is a separate application and requires a separate license, RapidMiner Server depends on RapidMiner Studio for operations. While you can run a process from RapidMiner Server, if you want to edit or change a process, you must make those changes through RapidMiner Studio. RapidMiner Server utilizes a home directory as a central place for server configuration and project content. |
| RapidMiner Job Agent | Job Agents are responsible to orchestrate execution on a node they are deployed. After an agent is running and connected to a queue it will start Job Containers whenever a process is available on the queue. |
| RapidMiner Job Container | Job Containers are responsible to execute a process. Their lifecycle is managed by the Job Agent which started them. |
| RapidMiner Server Projects | Also accessible from RapidMiner Studio, the RapidMiner Server project contains the RapidMiner Server processes and data. This content is stored within the home directory of RapidMiner Server. |
| Data sources | The individual user data sources, for example, those used for model building. Connections allow you to connect to databases or to connect to other data sources. Best practice suggests that you configure both RapidMiner Server and RapidMiner Studio with access to the data source. Connections to the data sources are used when building processes with operators such as Read Database or Write Amazon S3. |
| Operations database | The RapidMiner Server database stores configuration files, cron job details, you created report requests, and other internal RapidMiner data. The database is part of the AI Hub deployment and is not managed by the user) |
| Keycloak | The internal Keycloak service, which is responsible for user and group management. All users and groups used by RapidMiner Server are retrieved from this service |
| Keycloak database | The Keycloak database stores configuration, users and groups. The database is part of the AI Hub deployment and is not managed by the user) |
| Broker | The broker is the part of the deployment, which is responsible for managing queues between the components. It is part of the deployment and not manged by the user. |
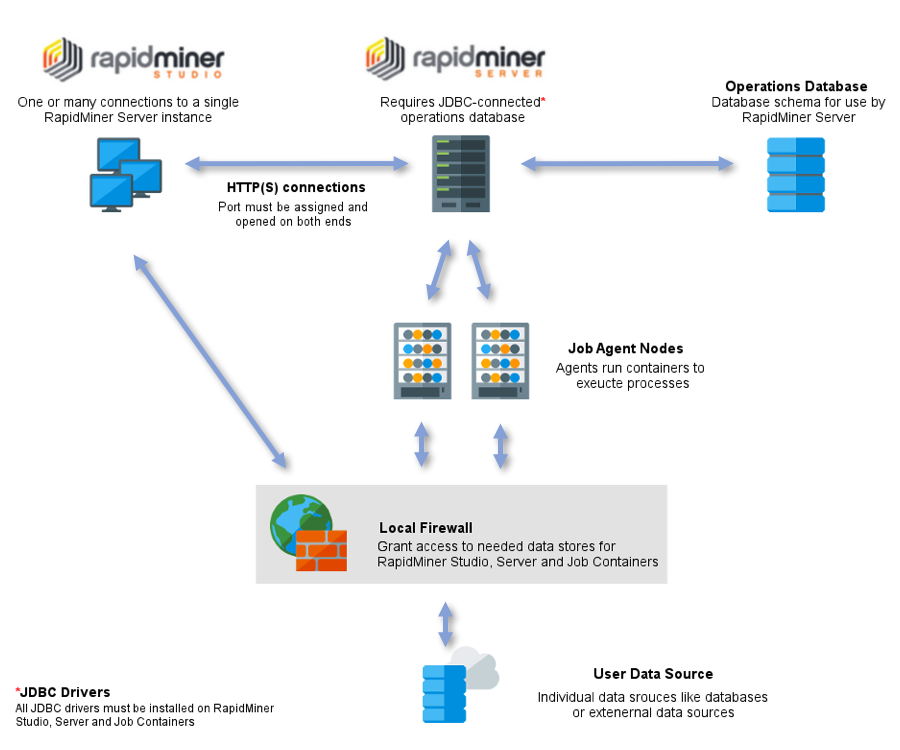
RapidMiner Studio and RapidMiner Server communicate via HTTP(S); you must assign and open the communication port on each instance in the configuration. Although true for any configuration, in the case of multiple clients, access rights management is particularly important for preventing unauthorized user access to repositories.
RapidMiner Server and Job Agents
RapidMiner Server outsources execution to an external entity called Job Agent. It does so by creating asynchronous queues to which it allows these agents to connect to.
Agents receive process messages via these queues and send back information about their own status, the status of the processes they are executing and process logs if requested. A Job Container
is spawned before each process execution, these containers run in their own JVM as a standalone OS process. The JVM terminates once the process has finished executing. To learn more about Job Agents, you can read the page
Installation > Job Agents, or read the README.md file inside the agent distribution.
Job Agents do not pick up existing executions in case they go down unexpectedly and boot up again. These executions have to be terminated manually by the administrator.
Using the RapidMiner Server projects
The RapidMiner Server projects, as with the local RapidMiner Studio projects, contain processes and data. This content is stored within the home directory of RapidMiner Server. Some details:
When you open the
 RapidMiner Server project in the Repository view of RapidMiner Studio, the platforms collaborate, making the data and process available to both applications.
RapidMiner Server project in the Repository view of RapidMiner Studio, the platforms collaborate, making the data and process available to both applications.You create processes in RapidMiner Studio and then save them to the
 RapidMiner Server project. They are available from both platforms.
RapidMiner Server project. They are available from both platforms.Those processes reference data sources, which can exist directly in the RapidMiner Server project, or can be referenced by connections that are used in operators.
Use the RapidMiner Server project in the same way as you use the RapidMiner Studio local project, although additionally, with correct permissions, users can share content.
Connecting to data sources
You can assign appropriate access rights instead of individually configuring those connections for each user on RapidMiner Server.
RapidMiner Studio accesses a data source directly and must have access to the data through any local firewalls. RapidMiner Server may access the data source directly or through RapidMiner Studio and also needs firewall access.
Both RapidMiner Studio and RapidMiner Server need to have any JDBC drivers that you use for a database connection. If you are using a driver that is not packaged with RapidMiner software, install it on both platforms.
See the section on creating connections for complete details.