You are viewing the RapidMiner Studio documentation for version 9.3 - Check here for latest version
Using the MySQL Connector/J (JDBC driver)
This guide targets the new Connection Management introduced with RapidMiner Studio 9.3.
For the old Legacy JDBC Connections see the 9.2 documentation
RapidMiner Studio comes bundled with the MariaDB Connector/J – a driver that allows to connect to both MariaDB and MySQL databases. If you want to connect to MySQL databases using the official driver, you need to manually download and configure the MySQL Connector/J.
This article will walk you through how to:
Download and extract the MySQL JDBC Connector/J
Download the latest Platform Independent release of MySQL Connector/J from the official MySQL website.
Both the compressed TAR archive and the ZIP archive will work.
The connector itself is a single file named mysql-connector-java-X.X.XX.jar.
Extract this file from the downloaded archive to a location on your hard drive that is accessible from RapidMiner Studio.
Create a new JDBC Connection
In RapidMiner Studio, right-click on the repository you want to store your Database Connection in and choose
 Create Connection.
Create Connection.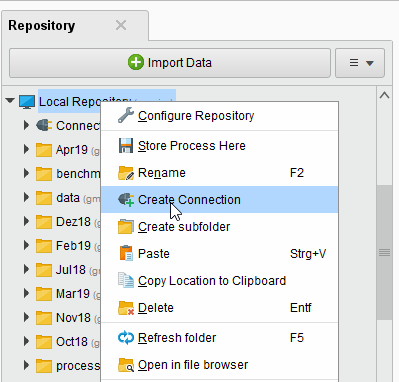
You can also click on Connections > Create Connection
 and select the repository from the dropdown of the following dialog.
and select the repository from the dropdown of the following dialog.Give a name to the new Connection, and set Connection Type to
 Database:
Database: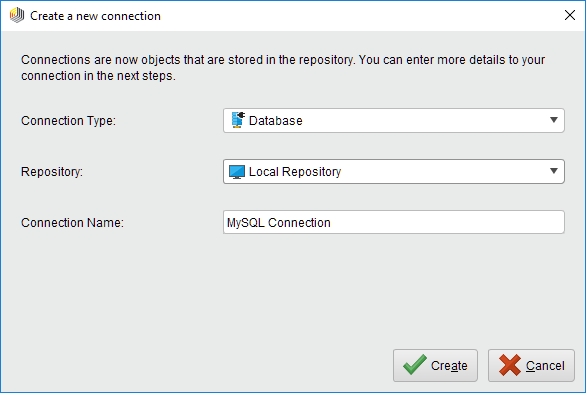
Select the Database system from the list of predefined DBs, or choose a custom system.
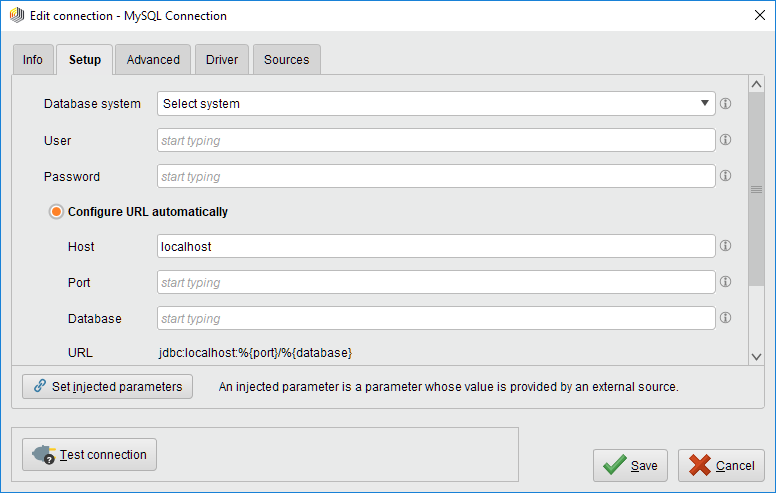
Fill out or adapt other necessary fields like User, Password, and Host.
(This step is only necessary if you have selected a Custom Database system). Go to the Driver tab and select the previous downloaded
mysql-connector-java-X.X.XX.jaras the JDBC driver Jar file. Note that the JAR file will be bundled inside the connection itself, so you can move or delete the downloaded file.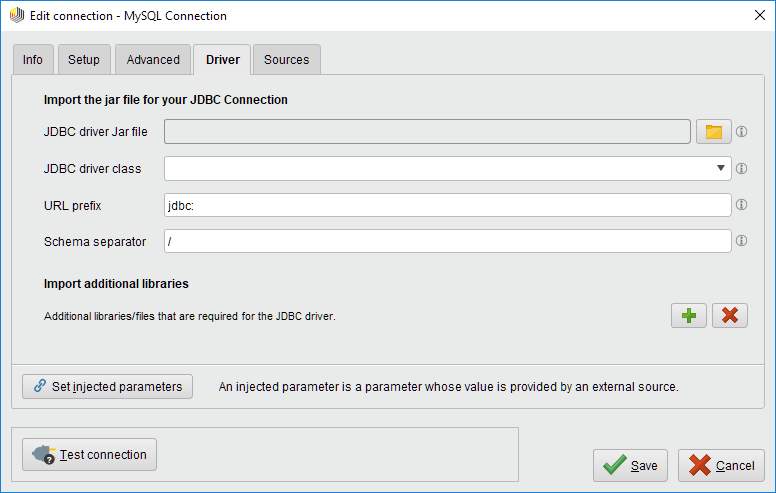
Use
 Test connection to check your settings by connecting to the database. After a successful test, you can close the dialog by clicking on
Test connection to check your settings by connecting to the database. After a successful test, you can close the dialog by clicking on  Save.
Save.
Use the JDBC connection
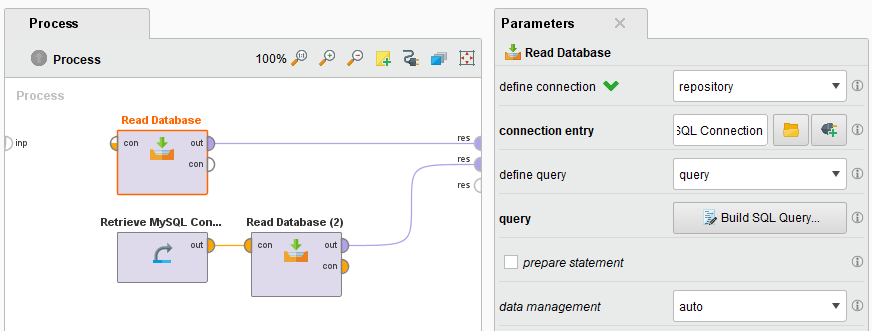
Use the newly created JDBC Connection with the Read Database, Write Database or Update Database operator.
In the following example the first Read Database operator uses the repository setting of define connection to select the connection entry by its path. While the second Read Database operator is directly connected to the connection with its connection input port.