You are viewing the RapidMiner Deployment documentation for version 9.6 - Check here for latest version
Python Environment Manager
Introduction
In RapidMiner platform deployments, we provide an Anaconda based Python environment, and the most recent version of the Python Scripting extension bundled with all your Job Agent containers. This can then be used by RapidMiner processes (containing Execute Python operators) executed on the scalable RapidMiner Server Execution Backend.
The goal of the Python Environment Manager is to ease the administration of these Python environments. Its key benefits are:
- reduced administrative overhead
- reduced risk of administrative errors
- ensured correct operation of deployed RapidMiner processes containing Python code
The Python Environment Manager is available as part of the RapidMiner platform deployment. See the deployment overview on where it fits in, and check one of the deployment templates to get started with it.
Limitations
Please be mindful of the following limitations when using Python Environment Manager:
- Python Environment Manager is available only in containerized RapidMiner deployments
- Python Environment Manager only manages Python environments shipped with the RapidMiner platform deployment.
- Python Environment Manager currently only manages Python environments for Job Agent based process execution. If you plan to use Execute Python operators as part of processes deployed as web services, you still need to manage your Python environments manually. Real-Time Scoring Agent is also not supported.
- When importing an environment definition file that was exported from another machine, only Linux (and WSL in Windows) is supported as a source. Environments exported from macOS or Windows based systems will not work. This is a limitation of the underlying Miniconda package manager.
Logging in and managing users
Initial login
Once deployed, you need to log in to the Python Environment Manager. The default URL to access the Python Environment Manager is on port 6080 of your RapidMiner deployment.
By default, there's an admin user created with a default password. The default password is dependent on the deployment method. For the cloud image based deployments, it's the intance ID (AWS) or the instance name (Azure). Otherwise, the default password is changeit.
Please make sure you change the initially provided password after the first login to ensure a secure operation.
User management and security
You can add and remove users by visiting the WebUI Access Control menu item.
You can also install an SSL certificate to facilitate encrypted communication between the browser and the Python Environment Manager. Click on the WebUI Certificates menu item and providing the certificate key and certificate file on the interface.
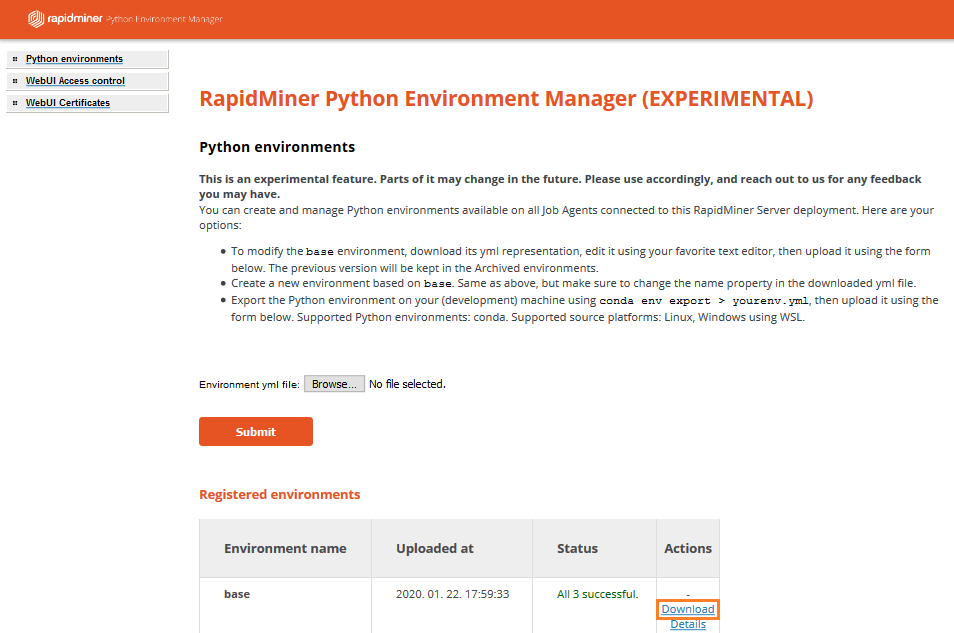
Creating a new Python environment
The Python Environment Manager interacts with a Miniconda installation present on the deployed Job Agents. It accepts environment definition YAML files which are used by Miniconda. Follow these steps to create a new environment:
- First, create a definition file on your computer. You can use any of the following methods:
- Preferred way: download the preinstalled base environment definition to your computer and edit it (be sure to change the name). See instructions below.
- Export the environment from your own machine using the
conda env exportcommand. Make sure to check the limitations first. - Open your favorite text editor and create the definition file manually.
- Preferred way: download the preinstalled base environment definition to your computer and edit it (be sure to change the name). See instructions below.
- In the Python Environment Manager UI, browse and find the YAML file you just created, and click Submit.
- Be patient for a few minutes until the settings are applied on all Job Agents.
- You can check the status of the deployment if you refresh the page.
Updating an existing Python environment
Updates are very similar to creating new environments. The only difference is that you need to specify an environment with an existing name. Follow the instructions above to create and upload your modified environment definition file.
Checking status and logs
You can track the status of an environment deployment by clicking on Details next to your environment. It will open a new page where you can see the stdout and stderr outputs for the conda commands executed on all connected Job Agents.
Downloading a Python environment definition file
You can download an existing environment definition file by clicking Download next to your environment.
Archiving an existing Python environment
If you no longer need an environment, you can archive it by clicking on the X next to your environment. This will remove the environment from all connected Job Agents, and move it to the list of archived environments in the Python Environment Manager. This might come in handy if you later need to reuse it or create a new one with slight modifications.
The base environment cannot be archived.
Managing archived environments
If you no longer need an archived environment for your records, you can completely erase it by clicking on the X next to the archived environment.
You can also erase all archived environments, by clicking on Remove all archived environments.