You are viewing the RapidMiner Studio documentation for version 9.7 - Check here for latest version
Using the Amazon S3 Connector
This guide targets the new Connection Management introduced with RapidMiner Studio 9.3.
For the old Legacy Amazon S3 connections see the 9.2 documentation
The Amazon S3 Connector allows you to access your Amazon S3 storage directly from RapidMiner Studio. Both read and write operations are supported. This document will walk you through how to:
Connect to your Amazon S3 account
To configure a new Amazon S3 connection you will need the connection details of your Amazon S3 account (at least the access key and the secret key).
In RapidMiner Studio, right-click on the repository you want to store your Amazon S3 connection in and choose
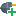 Create Connection.
Create Connection.
You can also click on Connections >
 Create Connection and select the repository from the dropdown of the following dialog.
Create Connection and select the repository from the dropdown of the following dialog.Enter a name for the new connection and set Connection Type to
 Amazon S3:
Amazon S3: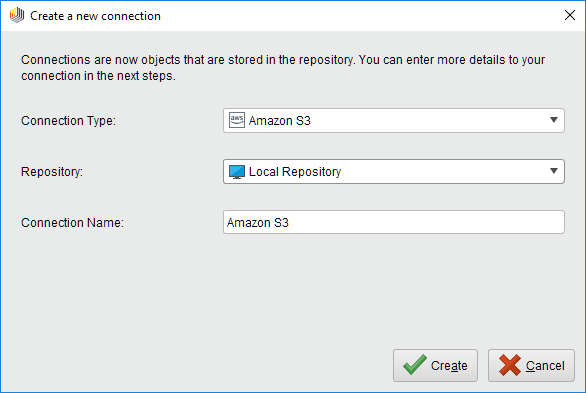
Click on
 Create and switch to the Setup tab in the Edit connection dialog.
Create and switch to the Setup tab in the Edit connection dialog.Fill in the connection details of your Amazon S3 account:
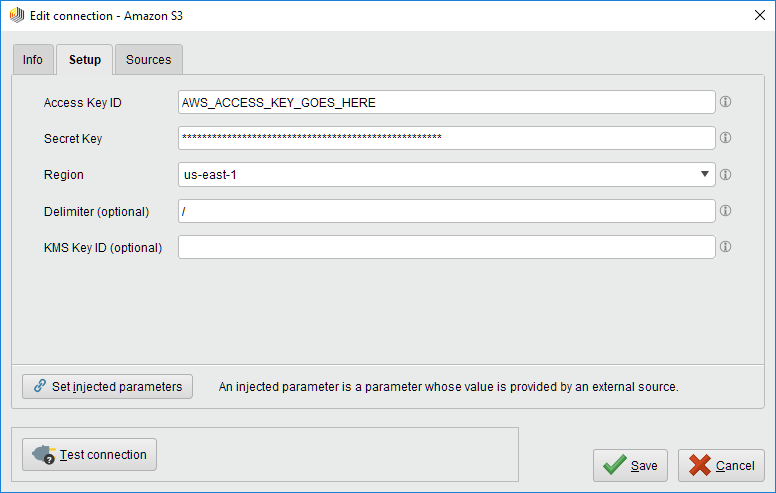
Note that Amazon S3 supports arbitrary folder "delimiters" (symbols to separate nested folders), e.g., "/" as used for URLs or "\" as used by Microsoft Windows. If the configuration specifies the wrong delimiter, your folder structure might not be displayed correctly in RapidMiner Studio. Don't worry though, you can always change the delimiter in the connection configuration later on.
While not required, we recommend testing your new Amazon S3 connection by clicking the
 Test connection button.
If the test fails, please check whether the details are correct.
Test connection button.
If the test fails, please check whether the details are correct.Click
 Save to save your connection and close the Edit connection dialog.
You can now start using the Amazon S3 operators!
Save to save your connection and close the Edit connection dialog.
You can now start using the Amazon S3 operators!
Read from Amazon S3
The Read Amazon S3 operator reads data from your Amazon S3 account. The operator can be used to load arbitrary file formats, since it only downloads and does not process the files. To process the files, you will need to use additional operators such as Read Document, Read Excel, or Read XML.
Let us start with reading a simple log file from Amazon S3.
Drag a Read Amazon S3 operator into the Process Panel. Select your Amazon S3 connection for the connection entry parameter from the Connections folder of the repository you stored it in by clicking on the
 button next to it:
button next to it: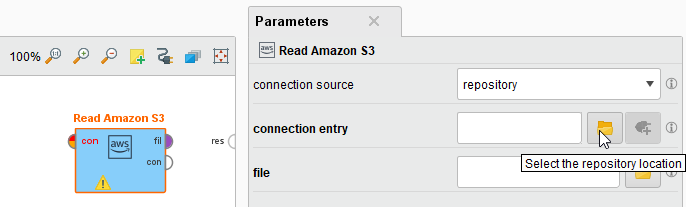
Alternatively, you can drag the Amazon S3 connection from the repository into the Process Panel and connect the resulting operator with the Read Amazon S3 operator.
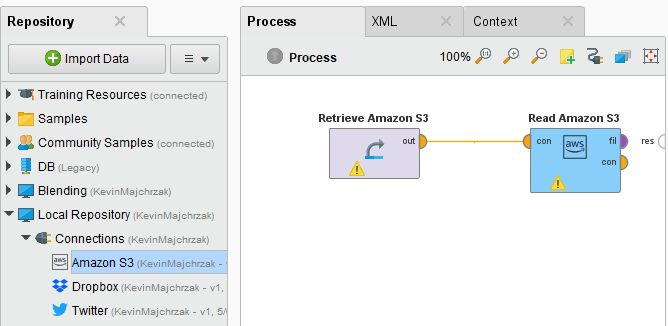
Click on the file chooser button
 to view the files in your Amazon S3 account.
Select the file that you want to load and click
to view the files in your Amazon S3 account.
Select the file that you want to load and click  Open.
Open.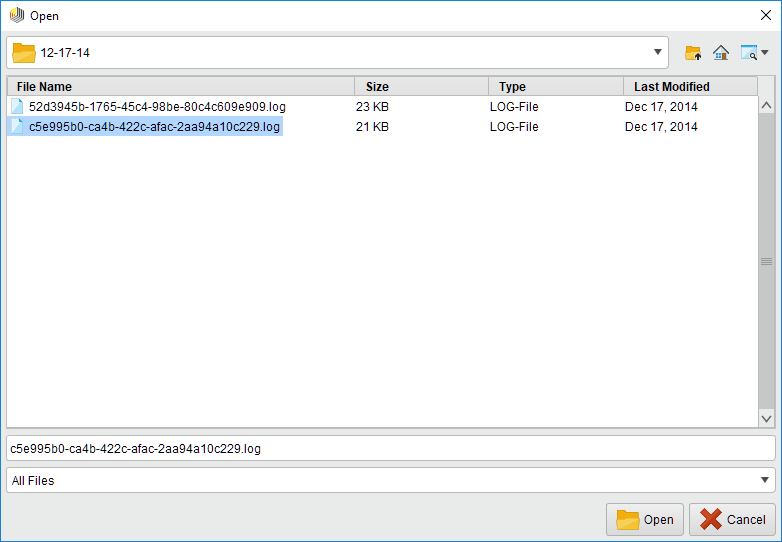
As mentioned above, the Read Amazon S3 operator does not process the contents of the specified file. In our example, we have chosen a log file (a plain text file). This file type can be processed via the Read Document operator which is part of the Text Processing extension for RapidMiner Studio.
If you have not already installed the Text Processing extension for RapidMiner Studio, please go to the marketplace and do so now. Then add a Read Document operator between the Read Amazon S3 operator and the result port:
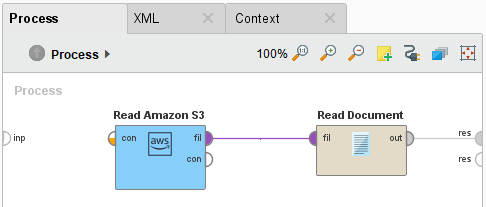
Run
 the process! In the Results perspective, you should see a single document containing the content of the log file.
the process! In the Results perspective, you should see a single document containing the content of the log file.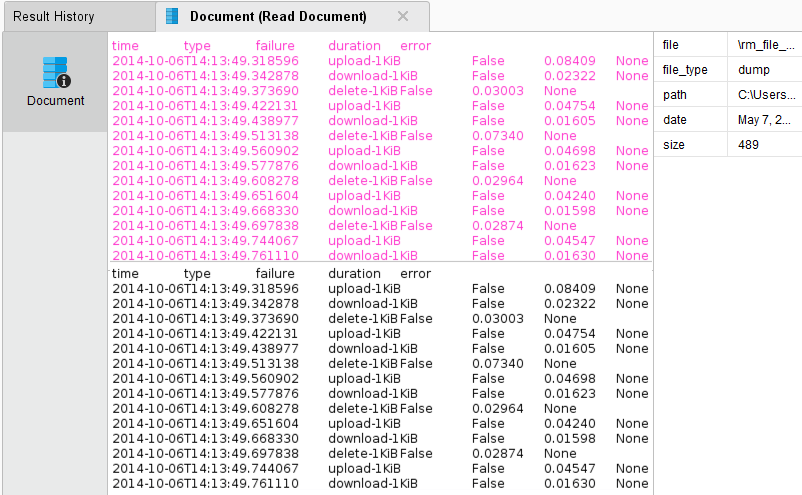
You could now use further text processing operators to work with this document, e.g., to determine the commonness of certain events. To write results back to Amazon S3, you can use the Write Amazon S3 operator. It uses the same Connection Type as the Read Amazon S3 operator and has a similar interface. You can also read from a set of files in an Amazon S3 directory, using the Loop Amazon S3 operator. For this you need to specify the connection entry and the folder that you want to process, as well the steps of the processing loop with nested operators. For more details please read the help of the Loop Amazon S3 operator.